Titanium is favored for its superior strength, light weight, and corrosion resistance and is used in a wide variety of industries. In this article, we will take an in-depth look at the properties of titanium, its different types, industry applications, and processing and manufacturing methods to help you better understand this important material.
1. Overview
What is Titanium?
Titanium is a lightweight metal with excellent strength and corrosion resistance, and is widely used in aerospace, medical, chemical and other applications.
Composition of Titanium.
The chemical symbol for titanium is Ti, and its atomic number on the periodic table is 22. Titanium exists mainly in the form of titanium ores such as ilmenite and titanium bauxite

Sources of Titanium.
The process of refining titanium usually involves converting titanium ore into titanium metal by smelting, commonly known as the Kroll process and lead smelting.

2. Different Types of Titanium
Titanium is categorized according to different criteria and is divided into the following main types and grades:

3. Properties of Titanium
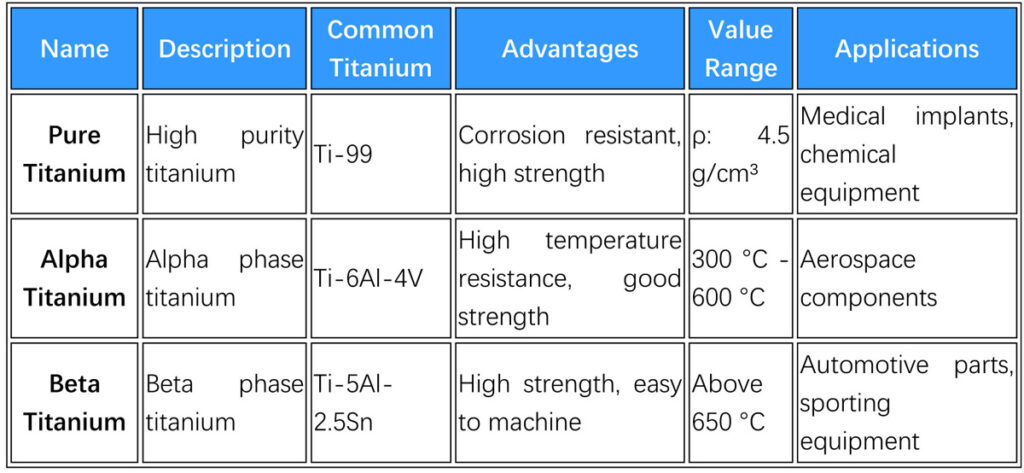
4. Industry Applications of Titanium
As a popular industrial material, titanium is widely used in several industries:
Aerospace
Due to its lightweight and high strength, titanium is commonly used in engine components and airframe structures to improve flight efficiency.
Medical
Titanium has good biocompatibility and is widely used in medical implants and surgical instruments to ensure safety and durability.
Chemical
Titanium’s corrosion-resistant properties make it highly sought after in the chemical industry, where it is commonly used in reactors and storage tanks to extend the life of equipment.
Automotive
In the automotive industry, titanium is used in the manufacture of body parts and exhaust systems to reduce vehicle weight and improve fuel efficiency.
Sports equipment
Titanium’s lightweight and strength properties make it ideal for sports equipment such as bicycle frames and titanium racquets, enhancing athletic performance.
5. Common Titanium Parts Processing and Manufacturing Methods
Allied Metal provides one-stop titanium parts machining services to meet your various needs.
6. Advantages and Disadvantages of Titanium in the Manufacturing Industry
Advantages
- High strength: Titanium has a very high strength-to-weight ratio, making it suitable for aerospace and other fields that require light weight.
- Corrosion resistance: Titanium remains stable in a wide range of environments, making it suitable for the chemical and medical industries.
- Biocompatibility: safe and reliable in medical applications.
Disadvantages
- High cost: Titanium is expensive to refine and process.
- Difficulty in processing: the hardness of titanium makes the process more complicated and requires special equipment.
- Difficulty in heat treatment: Titanium has a complex and demanding heat treatment process.
7. Summary
Titanium has become an indispensable material in modern manufacturing due to its unique lightweight properties and high hardness. Despite some challenges, titanium’s advantages have enabled it to remain in strong demand in high-end fields such as aerospace and medical.
Through continuous technological advances, the processing and application of titanium will continue to improve, offering more possibilities for future industrial development.



